New paper announcement
Insights into Superconductivity in ScRuSi
We are excited to announce that our latest research paper has been published in Phys. Rev. B, 109, 224517 (2024). This study offers a comprehensive investigation into the superconducting state of the ruthenium-based ternary equiatomic compound, ScRuSi.
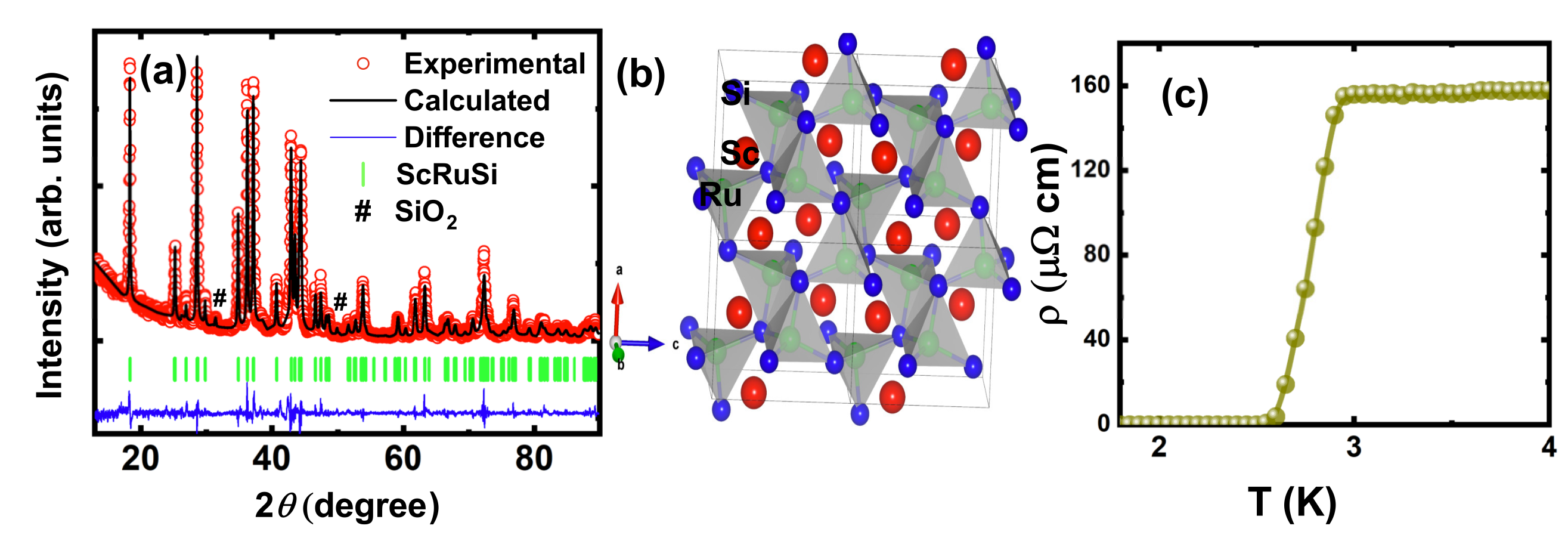 In our study, we explored the superconducting properties of ScRuSi using a combination of experimental techniques and theoretical calculations. Low-temperature resistivity measurements revealed a distinct superconducting phase transition in the orthorhombic structure of ScRuSi at a critical temperature (Tc) of 2.5K. Transverse-field muon spin rotation/relaxation (TF-muSR) analysis determined a gap-to-critical-temperature ratio of 2.7, aligning with previous heat capacity measurements. The temperature dependence of the superconducting normalized depolarization rate was fully described by the isotropic s-wave gap model. Zero-field muSR measurements indicated that the relaxation rate remains nearly identical below and above Tc, suggesting the preservation of time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state.
In our study, we explored the superconducting properties of ScRuSi using a combination of experimental techniques and theoretical calculations. Low-temperature resistivity measurements revealed a distinct superconducting phase transition in the orthorhombic structure of ScRuSi at a critical temperature (Tc) of 2.5K. Transverse-field muon spin rotation/relaxation (TF-muSR) analysis determined a gap-to-critical-temperature ratio of 2.7, aligning with previous heat capacity measurements. The temperature dependence of the superconducting normalized depolarization rate was fully described by the isotropic s-wave gap model. Zero-field muSR measurements indicated that the relaxation rate remains nearly identical below and above Tc, suggesting the preservation of time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state.
First-principles calculations using the McMillan-Allen-Dynes equation yielded a Tc of 2.1K, closely matching the experimentally determined critical temperature. The coupling between low-frequency phonon modes and the transition metal d-orbital states plays a crucial role in the superconducting pairing mechanism of ScRuSi.
The integration of experimental data with theoretical models allowed us to achieve a comprehensive microscopic understanding of the superconducting nature of ScRuSi. Our findings provide valuable insights into its critical temperature, pairing symmetry, and the underlying electron-phonon coupling mechanism.
We invite you to read the full paper to explore these findings in detail. Thank you for your continued support and interest in our research.